Competitive prices
Provide safe, comfortable and ethical dentistry
Friendly reception team
Preventative dentistry in Huddersfield
Netherton Dental Practice offers a range of preventive dentistry methods to all its patients. We have over 20 years of experience in the industry as dental practitioners.
Contact

Bad breath
Bad breath (or halitosis) is an unpleasant odour which can occur from time to time or be long lasting.
The main cause of bad breath is in the mouth. We have millions of bacteria that live in the mouth, particularly on the back of the tongue and these bacteria feed on the food debris that accumulates in the mouth and between our teeth. The bacteria give off a sulphur compound and it is this that creates the bad odour. Smoking and drinking alcohol contribute to the unpleasant odour. There are other conditions which affect the airways and stomach that can lead to bad breath too.
Improving your oral hygiene is the most effective way to eliminate bad breath. Brushing teeth and tongue twice a day using fluoride toothpastes, as well as flossing, will remove the bacteria which generally removes the odour. Other things that help are –
Drinking plenty of water
Chewing sugar free gum after meals
Stopping smoking
Eating a well balanced diet
Making regular visits to your dentist
The other causes of bad breath (which can be treated by your dentist) are
Chewing sugar free gum after meals
Stopping smoking
Eating a well balanced diet
Making regular visits to your dentist
The other causes of bad breath (which can be treated by your dentist) are
infection of the gums ( Periodontal disease )
decayed teeth
decayed teeth
a condition called ‘Dry mouth’ affecting the flow of saliva
If your dentist finds that your mouth is healthy but you still have bad breath, you may be referred to your family medical practitioner as there are other causes of bad breath -
Sinusitis and bronchitis.
Problems within the stomach.
Diabetes.
Liver and kidney problems.
Problems within the stomach.
Diabetes.
Liver and kidney problems.

Initial consultation
The first people you will meet will be our friendly reception staff, who will ask you to complete a medical form.
Our dentist needs to be aware of your general state of health as this can often impact upon the condition of your teeth and gums and may effect medication such as anaesthetics and antibiotics we may use for you.
At your consultation you will have the opportunity to discuss any dental concerns you may have or how you would like your teeth improved.
Your dentist will give you a full oral assessment to help accurately plan which treatments would be best for the health of your mouth. During this examination we will be looking at -
Teeth and the way you bite
Original restorations – Filling, crowns, veneers etc
The health of your gums and surrounding bone around each tooth
Your tongue, throat, cheeks & lips for signs of oral cancer
Jaw joint evaluation
Dental X-rays will also be taken of your teeth to check for -
Original restorations – Filling, crowns, veneers etc
The health of your gums and surrounding bone around each tooth
Your tongue, throat, cheeks & lips for signs of oral cancer
Jaw joint evaluation
Dental X-rays will also be taken of your teeth to check for -
Decay inside the tooth or between the teeth.
Abscess or cysts on the roots of your teeth.
Root positions
Bone loss
Abscess or cysts on the roots of your teeth.
Root positions
Bone loss
Once the examination is complete the dentist will dicuss the findings with you.
We will then create a treatment plan with alternative options for you, including all the benefits and risks of each procedure and the costings. This will allow you to decide what is best for your long term dental health.

Sports mouthguards
Mouthguards are made from a plastic material called Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). EVA is strong and tough and can be easily moulded to fit precisely over your teeth and gums.
Mouthguards are the most effective protective pieces of equipment to help prevent injury to the mouth - protecting the teeth, lips, cheeks and tongue. A mouthguard does not only protect your mouth, it can also cushion blows to the mouth or jaw therefore preventing damage to the jaw, neck or brain.
Having a dentist take special impressions will create a guard to perfectly fit your mouth, teeth and gums, providing ultimate protection. The procedure is very simple; your dentist will take moulds of your teeth both upper and lower. They will be sent to the dental laboratory where our technician will fabricate your custom made guard.
Your sports mouth guard will need replacing over time. Just bring it along to your check-ups and your dentist will inspect it for wear and tear.
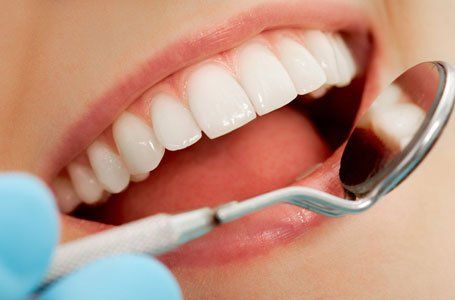
Oral hygiene
In order to keep your gums healthy you need to remove the daily build up of plaque from all the surfaces of your teeth by -
Pink in colour
No areas of redness or inflammation
No bleeding when brushing or flossing
No tenderness or discomfort
If the daily build up of plaque is not removed this can lead to the first stages of gum disease ‘Gingivitis’
Brushing your teeth twice a day, for two minutes each time. Ask your dentist which type of tooth brush is best for you, as many of us use brushes that are too hard or too large.
Clean in between your teeth, as a toothbrush doesn't always reach into the gaps in between the teeth or below the gum line.
Do not brush your teeth too hard as this can damage your gums, ask your dentist or hygienist to show you the correct technique
Use fluoride toothpaste.
Healthy gums are –
Clean in between your teeth, as a toothbrush doesn't always reach into the gaps in between the teeth or below the gum line.
Do not brush your teeth too hard as this can damage your gums, ask your dentist or hygienist to show you the correct technique
Use fluoride toothpaste.
Healthy gums are –
Pink in colour
No areas of redness or inflammation
No bleeding when brushing or flossing
No tenderness or discomfort
If the daily build up of plaque is not removed this can lead to the first stages of gum disease ‘Gingivitis’
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is caused by sticky bacteria which are known as ‘plaque’. Plaque collects in the small gaps between the gums and the teeth and if not removed by regular brushing & interdental cleaning will multiply by feeding on sugars found in your food and drink. This can lead to -
Bleeding when brushing or flossing
Soreness or discomfort
Soreness or discomfort
Appear red in colour, puffy or swollen
Bleeding when brushing or flossing your teeth is the earliest and most common sign of gingivitis. Gingivitis is reversible if treated by a hygienist or by improved brushing and flossing techniques. However, if left untreated you will develop the later stages of gum disease, which is known as ‘Periodontal Disease’.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal Disease is the later stages of gum disease. This is when the bacteria infection under the gums progresses deeper and affects the bone and tissue supporting the tooth.
Your gums will –
Bleed when brushing or flossing.
Will be red, swollen and tender.
Bad Breath.
The gum will have pulled away from the tooth, this is called ‘Pocketing’
Pus may be seen in the pockets around the tooth.
Will be red, swollen and tender.
Bad Breath.
The gum will have pulled away from the tooth, this is called ‘Pocketing’
Pus may be seen in the pockets around the tooth.
The infection damages the tissue that connects the gum to the roots of the tooth. Once the tissue has been destroyed the gum pulls away from the tooth, this forms a pocket which bacteria thrive in. If not treated, in time the bone anchoring the teeth in the jaw will dissolve, making the teeth loose and eventually the teeth will fall out
Periodontal disease is irreversible, but you can slow down the progression by regular visits to the Dentist and Hygienist also improving your oral hygiene at home.
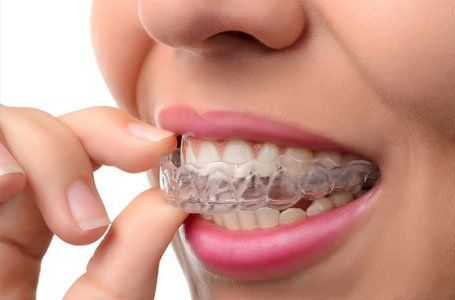
Grinding appliances
Teeth grinding is a surprisingly common occurrence and often happens whilst asleep. Most people are therefore unaware that they are grinding and only come to realise it when their partner complains of the noise the following morning.
Other noticeable effects of grinding (bruxism) are:
Ear ache
Jaw pain
Facial and neck pain
Sleep disorder - both yourself and partner
Sensitivity to hot and cold drinks
Jaw pain
Facial and neck pain
Sleep disorder - both yourself and partner
Sensitivity to hot and cold drinks
Why do we grind?
The most common reason for grinding is when we try and compensate for an imperfect bite. This is when the upper and lower jaw comes together but the teeth don’t seem to fit comfortably and you therefore try and force them into a perfect bite. Imagine chewing hard but with no food in your mouth.
You may also find that you suffer from jaw clenching, which if combined with grinding, will cause greater discomfort and damage to the teeth.
It is also thought that stress can lead to grinding although you may be equally unaware that you are doing so as it often happens during your sleep.
What are the consequences of grinding?
As you try to compensate for the imperfect bite you end up biting harder and thus causing damage to the enamel on your teeth. It becomes a vicious circle as you bite harder to try and make the teeth fit better you end up creating more damage to your teeth by initially wearing down the tooth’s enamel to gradually wearing down the tooth itself.
What can be done about it?
As most grinding occurs during your sleep, the most common solution is the use of a mouth guard to prevent such grinding. This helps reduce the pressure of tooth grinding and helps prevent further damage to your teeth. Your dentist may also be able make adjustments to your teeth order to achieve a better bite and thus reduce the subconscious effort you are making
Naturally, if your grinding is a result from stress then you should learn relaxation techniques and stress management.

Periodic examinations
The best way to maintain good oral hygiene is to brush and floss your teeth and to visit your dentist for regularly. Your dentist not only examines your teeth for signs of decay or damage, he also looks for early signs of gum disease and oral cancer.
It is normally recommended that you visit your dentist twice a year, although people who have severe gum disease or a weakened immune system may need to visit the dentist more often.
Your dentist will first ask if there have been any problems since your last dental check up and take a note of any new medication that you may be taking.
At your check up your dentist will :
Check for early signs of decay or breakages
Check existing restorations
Look at your gums for early signs of gum disease – this will be done using a probe which is gently placed between the tooth and your gum to determine the stage of gum disease
Examine your tongue, throat, cheeks & lips for signs of oral cancer
Examine jaw joint evaluation
Check existing restorations
Look at your gums for early signs of gum disease – this will be done using a probe which is gently placed between the tooth and your gum to determine the stage of gum disease
Examine your tongue, throat, cheeks & lips for signs of oral cancer
Examine jaw joint evaluation
X-rays of your teeth are usually taken every two to three years, unless your dentist notices a problem and needs an X-ray to look inside the tooth.
If cavities are found or your dentist feels that your oral hygiene needs to be improved, he will create a treatment plan outlining the work to be carried out and the costing; you will then need to make an appointment for the necessary treatment.
Occasionally, patients are referred to other dentists who specialise in the relevant fields of dentistry.

Periodontal disease
Periodontal Disease is the later stages of gum disease. This is when the bacteria infection under the gums progresses deeper and affects the bone and tissue supporting the tooth.
Bleed when brushing or flossing.
Will be red, swollen and tender.
Bad Breath.
The gum will have pulled away from the tooth, this is called ‘Pocketing’
Pus may be seen in the pockets around the tooth.
Your gums will –
Bleed when brushing or flossing.
Will be red, swollen and tender.
Bad Breath.
The gum will have pulled away from the tooth, this is called ‘Pocketing’
Pus may be seen in the pockets around the tooth.
The infection damages the tissue that connects the gum to the roots of the tooth.
Once the tissue has been destroyed the gum pulls away from the tooth,
this forms a pocket which bacteria thrive in. If not treated, in time the bone anchoring the teeth in the jaw will dissolve, making the teeth loose and eventually the teeth will fall out
Periodontal disease is irreversible, but you can slow down the progression by regular visits to the Dentist and Hygienist also improving your oral hygiene at home.

Root canal treatment
This dental procedure is carried out when the innermost part of the tooth ‘the pulp’ becomes badly decayed or infected. If left untreated, the tooth will begin to die which could lead to the loss of the tooth. To save the tooth, the infected pulp needs to be removed to prevent the formation of an abscess. In dental terms this procedure is called ‘Endodontics’
The tooth is made up of
- Enamel
– The hard outer layer of the tooth.
- Dentine
– This forms the core and gives the basic shape to the tooth which supports the enamel, it is softer than enamel but harder than bone.
- Pulp
– Is the central part of the tooth which contains nerves and blood vessels and lies within the root canal
The reason the pulp would die
- Caries
– If caries ‘decay’ is left it will travel through the enamel and dentine down into the pulp chamber.
- Trauma
– A severe knock that affects the pulp.
- Severe Gum Disease
- The gum detaches itself from the tooth creating a gap between the tooth and the gum, bacteria then gets trapped causing an infection which can infect the pulp.
The symptoms
- Pain
– This can be anything form a constant dull ache to severe pain or pain only when biting
- A spot
sometimes appears on the gum in the area of the infected tooth, this is where the collection of puss from the root tip is draining which will leave a bad taste in your mouth.
- Swelling
in the gum area surrounding your tooth
On your initial appointment the dentist will locate the offending tooth and take an x-ray in order to show the roots of the tooth, to see how far the decay has travelled and if there is an abscess present. A course of antibiotics may be given to clear the abscess before the treatment is started as the abscess will reoccur if the treatment is NOT carried out.
The first appointment
- The dentist will give you a local anaesthetic to numb the tooth and the area surrounding it.
- Your tooth will then be isolated from the rest of your teeth using a ‘rubber dam’ which is a thin sheet of rubber placed over your mouth. It is used to keep the tooth dry as saliva has bacteria present which can infect the tooth. It is also used to protect your airway as the instruments used to clean the canals are very small.
- Your dentist has to gain access to the pulp chambers, this is done by drilling a hole in the top of your tooth.
- Once access has been gained to the pulp chambers the dead pulp is removed from the root canals using very small files and a hydrochloric wash. An additional x-ray will be taken at this point.
- Once the root canals are cleaned the dentist will place a medication to help clear any bacteria. The tooth will then either be temporarily filled and another appointment required or if the infection was not too serious, the tooth can be filled permanently and your treatment complete.
- The tooth may feel tender for a few days and you may need to take pain killers
If a second appointment is necessary
- You will be given a local anaesthetic to numb tooth and the surrounding tissue
- The rubber dam will be placed and your temporary filling will be removed.
- The dentist will continue cleaning out the canals using the same process as before. Once the canals are clean and dry they will be filled with a material called ‘Gutta Percha’ which is placed into the root canal until it is sealed.
- An X-ray is then taken to check that the canals have been filled completely.
- A permanent filling will then be put in place.
- Your dentist may advise you to have a crown placed on the tooth to strengthen it.

For all your preventative dentistry, call us on
01484 661 277
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Oops, there was an error sending your query.
Please try again later
Email us
Share
Tweet
Share
Mail
Phone: 01484 661 277
Email:
Address:
Netherton Dental Practice
362 Meltham Road
Huddersfield
West Yorkshire
HD4 7EH
© 2024. The content on this website is owned by us and our licensors. Do not copy any content (including images) without our consent.




